Audio By Carbonatix
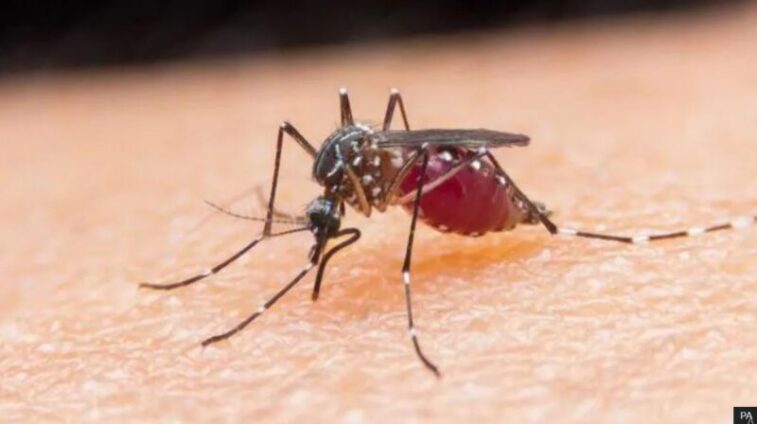
Scientists believe they have found a quirky way to fight mosquito-spread diseases such as dengue, yellow fever and Zika - by turning male insects deaf so they struggle to mate and breed.
Mosquitoes have sex while flying in mid-air and the males rely on hearing to chase down a female, based on her attractive wingbeats.
The researchers experimented, altering a genetic pathway that male mosquitoes use for this hearing. The result - they made no physical contact with females, even after three days in the same cage.
Female mosquitoes are the ones that spread diseases to people, so trying to prevent them from having babies would help reduce overall numbers.
The team from the University of California, Irvine studied Aedes aegypti mosquitoes, which spread viruses to around 400 million people a year.
They closely observed the insects' aerial mating habits - which can last between a few seconds to just under a minute - and then figured out how to disrupt them using genetics.
They targeted a protein called trpVa that appears to be essential for hearing.
In the mutated mosquitoes, neurons normally involved in detecting sound showed no response to the flight tones or wingbeats of potential mates.
The alluring noise fell on deaf ears.
In contrast, wild (non-mutant) males were quick to copulate, multiple times, and fertilised nearly all the females in their cage.
The researchers from the University of California, Santa Barbara, who have published their work in the journal PNAS, said the effect of the gene knock-out was "absolute", as mating by deaf males was entirely eliminated.
Dr Joerg Albert, from the University of Oldenburg in Germany, is an expert on mosquito mating and I asked him what he made of the research.
He said attacking sense of sound was a promising route for mosquito control, but it needed to be studied and managed.
"The study provides a first direct molecular test, which suggests that hearing is indeed not only important for mosquito reproduction but essential.
"Without the ability of males to hear - and acoustically chase - female mosquitoes might become extinct."
Another method being explored is releasing sterile males in areas where there are pockets of mosquito-spread diseases, he added.
Although mosquitoes can carry diseases, they are an important part of the food chain - as nourishment for fish, birds, bats and frogs, for example - and some are important pollinators.
Latest Stories
-
Kofi Adams pledges welfare support for retired footballers
30 seconds -
Unpaid Nurses, Midwives allege salary arrears vanished from payment records
14 minutes -
Stadium violence: Six SHS students arrested in Ashanti Region
21 minutes -
Fishermen still at sea after armed raid, rescue teams mobilised
24 minutes -
Elite Teachers group endorses Prof. Opoku-Agyemang for NDC 2028 flagbearer race
53 minutes -
The economics of being an artiste in Ghana
55 minutes -
North Korea could ‘get along’ with US, says Kim Jong Un
57 minutes -
AngloGold Ashanti Obuasi certifies 100 Youth artisans through skills programme
58 minutes -
Nigeria to hold inquest into death of Chimamanda Ngozi Adichie’s toddler
1 hour -
Hong Kong tycoon Jimmy Lai wins appeal against fraud conviction
1 hour -
Grand visions, little execution: The cost of inaction in Ghana’s music industry
1 hour -
CID and Military Police renew collaboration to tackle emerging crimes
1 hour -
Makola No. 2 traders protest against high Rents and new 20% VAT
1 hour -
24-Hour economy won’t work without solid economy—Hamza Suhuyini
2 hours -
If you cheat, God will judge you – Rev. Daniel Annan warns
2 hours