
Audio By Carbonatix
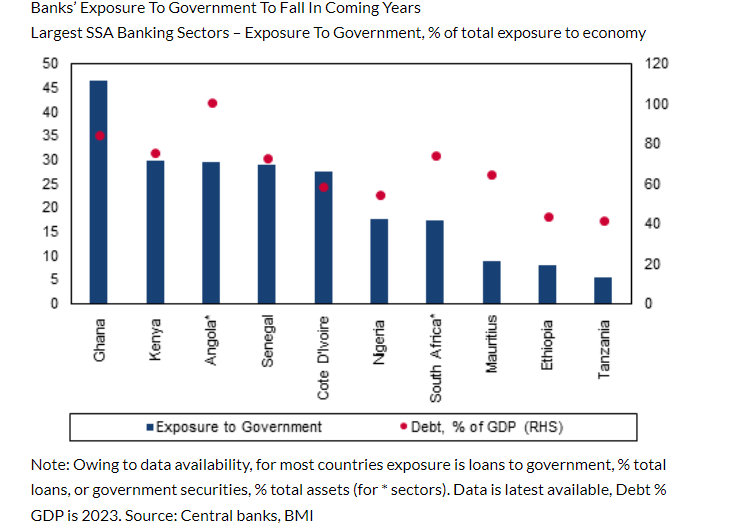
Ghana recorded the highest banks’ holdings of government debt in Sub Saharan Africa in 2023, Fitch Solutions has revealed.
In terms of government debt to Gross Domestic Product (GDP), the country came second behind Angola.
Kenya, South Africa and Senegal came 3rd, 4th and 5th respectively.
The report said banks in Sub-Saharan Africa including Ghana will continue to face risks associated with sovereign exposure throughout the forecast period. Nonetheless, these risks are expected to diminish over time.
During the Covid-19 pandemic, banks’ holdings of government debt and claims to the public sector surged as governments increased borrowing to fund additional expenditures.
With limited access to international markets owing to prohibitive costs, the report, said domestic banks became the main financiers. This dependence, it added, poses significant risks to banks, particularly when government finances are strained.
“This dependence poses significant risks to banks, particularly when government finances are strained. For instance, Ghana's default on its domestic and external debt in December 2022 led to considerable losses for banks participating in its domestic debt exchange programme”.
“As can be seen in the chart below, banking sectors in markets with elevated levels of government debt typically have the highest exposure to the government through loans or government securities holdings. We expect that the average debt-to-GDP ratio for the region will fall in the coming years, after peaking in 2023, boding well for our view that banks will reduce exposure to the sovereign”, it stressed.
Reopening of Africa’s Eurobond market in 2024 marks positive shift
The report continued that the reopening of Africa's Eurobond market in 2024, following a hiatus of more than a year, marks a positive shift, with successful, oversubscribed bond issuances from countries such as Côte d'Ivoire, Benin, and Kenya.
This resurgence, it said, provides government with a source of financing other than banks, offering banks the opportunity to lessen their exposure to sovereign debt, potentially liberating resources for increased lending to the private sector. However, this transition is expected to be gradual, as loan quality continues to be a concern and private sectors present higher risk profiles than sovereigns.
Latest Stories
-
Ghana Water targets the end of January 2026 to resolve Teshie water crises
2 hours -
All UG students who overpaid fees will be refunded – Deputy Education Minister
3 hours -
Majeed Ashimeru set for La Louvière loan switch from Anderlecht
3 hours -
NPP flagbearer race: Any coercion in primaries will be resisted – Bryan Acheampong campaign team
3 hours -
‘Infection spread’ feared: Teshie water crisis triggers healthcare emergency
3 hours -
AratheJay turns ‘Nimo Live’ into defining homecoming moment
4 hours -
NPP race: No official complaint over N/R allegations – Haruna Mohammed
4 hours -
Security analyst warns protocol recruitment eradication will not happen overnight
4 hours -
KGL Foundation commissions ultra-modern Gloria Boatema Dadey-Nifa Basic School at Adukrom
5 hours -
GIMPA reveals GH¢1.7m debt from defaulting sponsored lecturers
5 hours -
PAC cites five GIMPA lecturers for GH¢1.7m bond default
5 hours -
Google confirms that it won’t get Apple user data in new Siri deal
6 hours -
Gomoa Central Special Economic Zone to become first major industrial hub in Central Region – Vice President
6 hours -
Carlos Alberto Pintinho: The ex-Sevilla star who can never play football again
6 hours -
UBA Ghana names Bernard Gyebi Managing Director as bank reorganises top leadership
6 hours

