
Audio By Carbonatix
Africa’s debt sustainability has become a pressing concern, advisory firm, Bridgewater Advisors has stated in its Africa Economic Outlook.
According to the firm, the continent’s public debt between 2010 and 2024, surged by a staggering 170%, partly due to the global financial crises, Covid-19, and geopolitical tensions.
In comparison, global public debt rose by just 54% over the same period. These debt burdens have been further exacerbated by recent exchange rate depreciations, which have significantly increased debt repayment burdens.
Compounding this, it said, is an international financial architecture ill-equipped to offer affordable liquidity at scale to close Africa’s developmental gap.
In a bid to turn the tide, African leaders have approved the establishment of the African Financial Stability Mechanism (AFSM), a $20 billion fund hosted by the African Development Bank. This facility aims to avert future debt crises by offering concessional financing to member states that commit to prudent macroeconomic and fiscal reforms.
The AFSM is anticipated to save African countries approximately $20 billion in debt servicing costs by 2035. While the AFSM offers a safety net, it is not a definite solution.
“Achieving lasting debt sustainability will require coordinated action across the continent, anchored in robust macroeconomic management, strengthened fiscal discipline, and improved domestic revenue mobilization, Prosper Melomey, Partner, Corporate Transactions & Investment Bank, Africa stated.
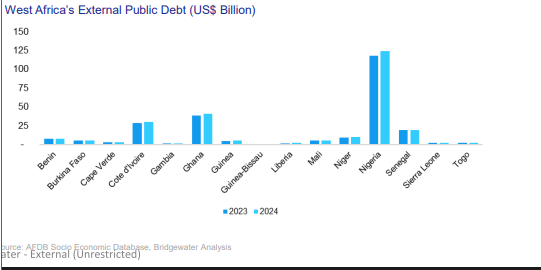
Ghana recorded $6bn debt increase in 2024
West Africa maintained a stable fiscal position with external debt-to-GDP ratio of 31%, despite a 5% rise in external funding.
However, Ghana and Nigeria recorded the highest nominal debt increases of $6 billion and $2.5 billion, respectively in 2024.
Nigeria accounted for about 48% of the region’s total external debt.
Bridgewater Advisors continued that Africa's external debt outlook for 2025–2026 remains high, with Southern Africa seeing the highest debt levels, rising from 30% to 31% driven by South Africa’s fiscal pressures and Zambia’s restructuring challenges.
East, North, and West Africa maintain stable debt at 22%, while Central Africa has the lowest at 3%. Debt sustainability remains a concern, especially in high borrowing regions like Southern Africa.
Latest Stories
-
Karaga MP donates 4,000 gallons of fuel to boost livelihoods in New Year outreach
2 hours -
GIPC CEO engages European Parliament delegation on Ghana’s investment reforms
2 hours -
BoG rejects market speculation, emphasises data-driven policies
3 hours -
BoG targets consolidation, discipline in 2026 policy direction
3 hours -
GJA-Ashanti commends EPA’s continuous engagement with journalists who were involved in accident
3 hours -
Wenchi needs development, help us – Chiefs to Aseidu Nketia
4 hours -
EPA boss encourages journalists not to relent in their support to fight galamsey
4 hours -
Domestic Gold Purchasing Programme helped Ghana’s economy during difficult period – IMF
4 hours -
Ike City Group of Companies touches hearts at Dzorwulu Special School with compasionate donation
5 hours -
Vehicle exhaust pipes on the left create about 40% more pollution on the road than those on the right – Study
5 hours -
My Response to Dr Bryan Acheampong: Facts must prevail
5 hours -
U.S. and Ghana Armed Forces strengthen medical readiness at SETAF-AF Best Medic Competition
5 hours -
Earlier passage of BoG’s Amendment Bill could have prevented haircuts – Dr. Asiama
6 hours -
Economic stability gains were hard-won through discipline and institutional effort – BoG Governor
6 hours -
GCB Bank rewards customers at first “Pa To Pa” Promo Draw
6 hours

