Audio By Carbonatix
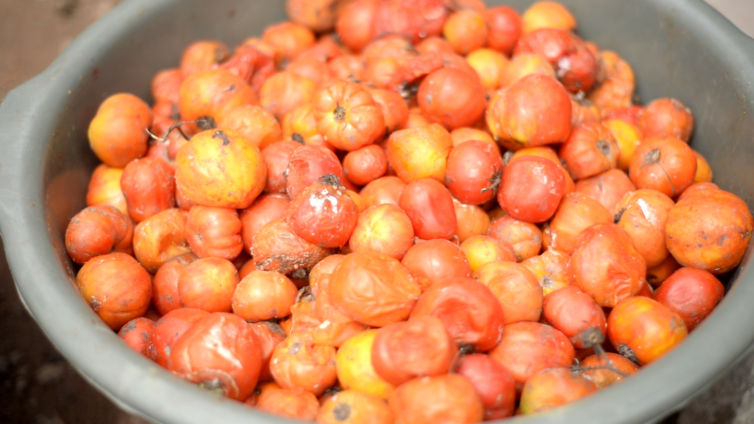
Consumption of spoiled tomatoes is on the increase with more patronage by some commercial food operators in Ghana.
Spoiled tomatoes may have higher nutritional and healthful plant-based chemicals than fresh tomatoes but are highly contaminated with harmful microbes, thus not safe for consumption.
That is the conclusion of a study by the Kwame Nkrumah University of Science and Technology (KNUST), Kumasi, with sponsorship from the Foundation for Food and Agriculture Research and Rockefeller Foundation.
Consumption of tomatoes provides health benefits. However, they’re highly perishable due to their high moisture content, soft nature, postharvest handling and are highly prone to microbial contamination.
The study was undertaken to determine the nutritional and phytochemical compositions of fresh and spoiled tomatoes. In addition, the researchers also sought to determine the levels of microbial load in sampled tomatoes.
For the study, fresh tomatoes and spoiled tomatoes were obtained from different tomato sellers at Borla Market in Kumasi in the Ashanti region of Ghana and analysed.
The researchers found all the spoiled tomatoes had considerably higher levels of nutrients (crude fibre, higher potassium, and high folic acid) as compared to the fresh tomatoes except for moisture and vitamin C.
Again, higher levels of plant-based chemicals known as phytochemicals were found in the spoiled tomatoes, particularly lycopene, beta carotene and chlorogenic acid.
The researchers attribute the results to advance ripening and moisture loss in spoiled tomatoes.
“As ripening goes on, these phytonutrients are synthesized,” lead scientist Prof. Faustina Dufie Wireko-Manu of the KNUST Food Science and Technology said.
The researchers, however, warn spoiled tomatoes are highly contaminated with harmful microbes.
“We found the spoiled tomatoes were contaminated with molds, E Coli and other harmful bacteria, beyond recommended levels by Foods and Drugs Authority (FDA).
"They’re highly contaminated with microbes and therefore not safe for human consumption,” explained Prof. Faustina Dufie Wireko-Manu.
Latest Stories
-
University of Ghana gears up for Telecel TurnUp on Val’s Day
3 minutes -
Violence against women is an economic catastrophe – President Mahama
8 minutes -
Contractor offers to repair damaged sections of Agona Nkwanta–Tarkwa Road Corridor at own cost
10 minutes -
Sinapi Aba Trust graduates 247 youth under its apprenticeship programme
11 minutes -
Concerned Farmers Association to announce position on new cocoa prices next week
16 minutes -
UNICEF encourages World Vision Ghana to remain a strong voice for children
20 minutes -
RTI Law: A triumph of legislative intent, tragedy of implementation
21 minutes -
Over 7,000 Muslims benefit from KSrelief food basket initiative in Ghana
28 minutes -
Sunda Group supports government’s free sanitary pad initiative with 10,000 packs
54 minutes -
“Everybody looks at me differently; some say I’m pretty” – Abigail Anderson opens up on living with vitiligo
1 hour -
President Trump’s moment of opportunity and the world at a crossroads
1 hour -
Ghana Cocoa board moves toward economic independence amid $2.5 billion debt crisis
1 hour -
AGA Obuasi Mine & partners inspire girls at Asare Bediako SHS to pursue careers in STEM
1 hour -
The 2026 WAFCON tournament will continue – CAF
2 hours -
Ministry of Youth Development urges responsible celebrations ahead of Valentine’s Day
2 hours

