
Audio By Carbonatix
Ghana’s central bank will need to raise interest rates further this year unless a decline in the cedi is arrested, Goldman Sachs Group Inc. and Absa Group Ltd. said.
The West African nation increased borrowing costs by the biggest margin in two decades on Monday to arrest inflation that accelerated at the fastest pace in almost six years in February and stem a depreciation in the cedi. The currency has weakened more than 17% against the dollar this year, making it the worst performer on the continent.
Finance Minister Ken Ofori-Atta is preparing to unveil measures this week aimed at supporting the cedi, ensuring expenditure discipline and providing relief to the economy, the Information Ministry said. It didn’t provide further details.
“If these measures fail in turning the economy around or fall short of its ultimate objectives, including stabilizing the exchange rate or reversing the recent sharp depreciation, we believe a further policy rate hike” of 100 basis points is likely by the third quarter, Ridle Markus, a Johannesburg-based Africa strategist at Absa, said in a note to clients.
The cedi strengthened 0.1% to 7.36 per dollar by 10 a.m. in London.
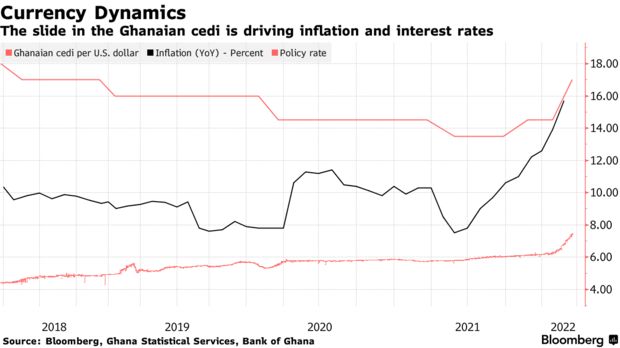
Ghana’s currency has slumped this year amid concern the nation won’t achieve its revenue and debt targets, which has sparked a selloff of its foreign-currency debt. Inflation is surging in part because of the impact of the war in Ukraine on global energy and food prices. Ghana imports about a third of its grain needs and almost 40% of its fertilizer requirements from Russia, according to the central bank.
The government in January moved to reassure investors that it’s committed to fiscal targets, including expenditure cuts if revenue falls short of expectations. Ofori-Atta has yet to get parliament’s approval to introduce a so-called e-levy on financial transactions that’s aimed at helping boost tax revenue to 15.4% of gross domestic product this year from an estimated 12% last year.
“The fact that the government has so far failed to pass the budget that it proposed in November, including new revenue measures -- implying likely fiscal slippage -- adds to Ghana’s rising risk premium,” Goldman economists Bojosi Morule and Andrew Matheny said in an emailed note.
That combined with tightening financial conditions for emerging-market countries due to the war in Ukraine “add to the already meaningful depreciation pressures” on the cedi and increase the risk of further hikes, they said.
Ghana’s monetary policy committee is scheduled to announce its next rate decision on May 23.
Latest Stories
-
Zambia scraps taxes on Fugu from Ghana for personal use following social media drama
41 minutes -
Gunfire silences prosperity as PLO Lumumba warns of ‘bleeding’ African continent
2 hours -
African Leaders must shift from speeches to action – P.L.O Lumumba
3 hours -
Ace Ankomah demands radical overhaul of Ghana’s science and innovation sector
3 hours -
Trump signs executive order threatening tariffs for countries trading with Iran
3 hours -
From Hollywood to the homeland: Why African countries are courting black American stars
3 hours -
Ambulance service slams ‘taxi transfer’ of newborn as viral negligence claims debunked
4 hours -
High stakes in Ayawaso East as NDC delegates head to the polls today
4 hours -
Youth unemployment is the biggest threat to Africa – Gabby
4 hours -
Minority demands urgent Finance Minister summons as ‘Agbogbloshie’ prices ignite parliamentary clash
5 hours -
Baba Jamal’s highest will be 38% in Ayawaso East NDC primary – Mussa Dankwah
6 hours -
Stranded beans and staggering debts: Ghana’s cocoa sector faces systemic crisis
6 hours -
Chief Justice sets up special courts for corruption and galamsey
6 hours -
Airport renaming and inflation trends to take centre stage on Joy Prime’s Prime Insight this Saturday
7 hours -
Ghana losing long-term investment capital over absence of Limited Partnerships Law – GVCA CEO
8 hours

