Audio By Carbonatix
The Ghanaian economy is currently navigating a critical phase of recovery, marked by a decisive shift towards fiscal consolidation and monetary easing.
The net effect of recent policy changes specifically; the increase in utility tariffs, stabilization of the cedi, reduction in fuel prices, and comprehensive tax reforms (including the removal of the flat 3% VAT rate and the COVID-19 levy), is a projected stabilization of the macroeconomic environment.
While the upward adjustment of utility tariffs introduces inflationary pressure, this is largely counterbalanced by the positive impacts of a stable currency, declining inflation, and a subsequent reduction in interest rates, which collectively foster a more favourable climate for private sector growth and investment.
Macroeconomic Context and Trends
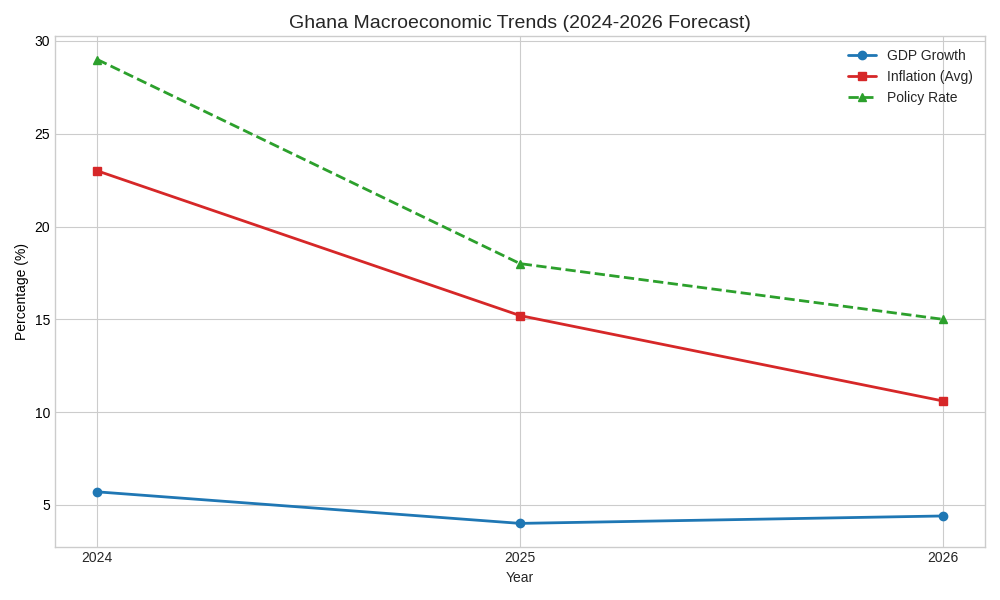
The economic outlook for Ghana is characterized by a strong disinflationary trend and a return to moderate, sustainable growth. The data below illustrates the projected trajectory of key indicators.
| Indicator | 2024 (Actual/Est) | 2025 (Forecast) | 2026 (Forecast) | Primary Driver |
| Real GDP Growth | 5.7% | 4.0% | 4.4% | Fiscal consolidation and private sector recovery [4] |
| Average Inflation | 23.0% | 15.2% | 10.6% | Monetary policy tightening and cedi stability [5] |
| Monetary Policy Rate | 29.0% | 18.0% | 15.0% | Response to falling inflation [6] |
| Cedi Stability | Volatile | Improving | Stable | Improved reserves and debt restructuring [7] |
The most significant development is the rapid deceleration of inflation, which fell to 6.3% in late 2025, a level not seen since early 2019 [8]. This success has enabled the Bank of Ghana to implement aggressive cuts to the Monetary Policy Rate, which stood at 18% in November 2025, signaling a lower cost of borrowing for businesses and consumers in 2026 [6].
Macroeconomic Trends Visualization
The following chart visualizes the projected convergence of the Monetary Policy Rate and Inflation, a key indicator of economic normalization.
Analysis of Policy-Specific Impacts
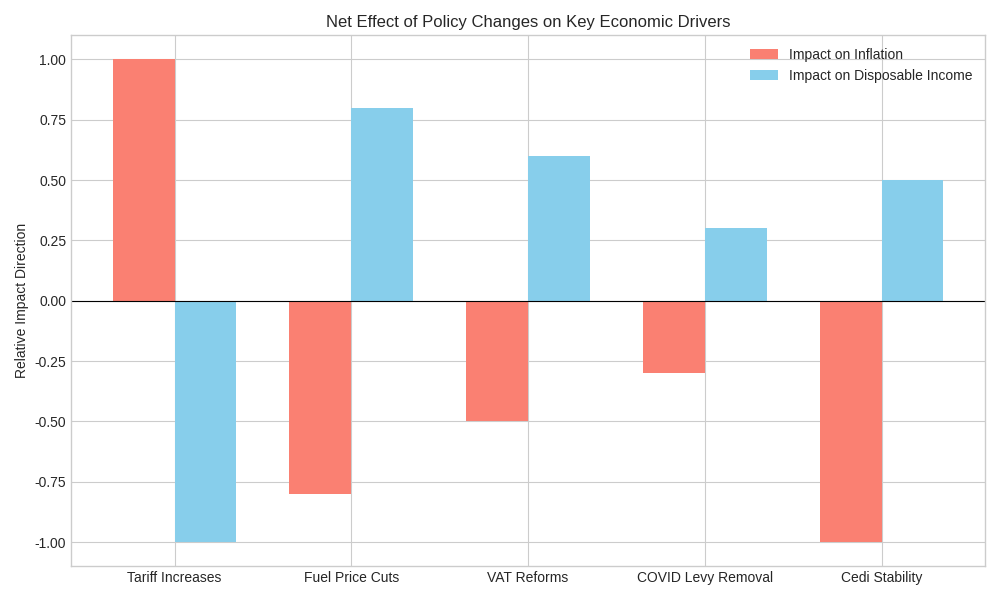
The net effect on the economy is a result of the interplay between contractionary and expansionary forces from the new policies.
- Tax Reforms: Removal of Flat 3% VAT Rate and COVID Levy
The government's "Fiscal Reset" includes a comprehensive overhaul of the Value Added Tax (VAT) regime, effective from 2026 [1].
| Policy Change | Direct Impact | Economic Effect |
| Abolition of COVID-19 Levy | Removes a 1% levy on the supply of goods and services. | Reduces the effective tax burden on businesses and consumers, contributing to disinflation [1]. |
| Removal of Flat 3% VAT Rate | Reverses the flat rate regime, allowing businesses to claim input VAT deductions. | Eliminates the cascading effect of taxes, lowering the cost of production and improving business competitiveness [1]. |
| Effective VAT Rate Reduction | Overall effective VAT rate reduced from ~21.9% to 20%. | Increases disposable income for households and stimulates consumption [1]. |
The net effect of these tax reforms is expansionary and disinflationary, providing relief to the private sector and supporting the government's goal of improving the ease of doing business.
- Tariff Increases and Fuel Price Dynamics
A major counter-inflationary force is the increase in utility tariffs, which is necessary for the financial viability of the energy sector.
- Utility Tariffs: Electricity and water tariffs saw significant hikes in early 2026 (9.86% and 15.92% respectively), following cumulative increases in 2025 [9]. These increases raise the cost of living and production.
- Fuel Prices: Conversely, fuel prices have seen a marginal decline in early 2026, driven by the appreciation of the Cedi and stable global oil prices [10].
- Net Effect: The reduction in fuel prices, a major component of the transport and logistics cost structure, acts as a crucial offset to the inflationary impact of higher utility tariffs. The overall impact on the Consumer Price Index (CPI) is likely to be dampened by the fuel price relief.
- Stable Currency (Cedi)
The stability of the Ghanaian Cedi is arguably the most critical factor in the current economic outlook.
- Impact: A stable Cedi reduces the cost of imported goods, particularly fuel and raw materials, which are major drivers of domestic inflation [7]. This stability reinforces the disinflationary trend and allows the central bank to continue its rate-cutting cycle.
- Net Effect: The stable currency provides a strong anti-inflationary anchor for the entire economy, mitigating the price pressures from domestic tariff increases.
Overall Net Effect
The overall net effect is a positive shift towards macroeconomic stability, driven by the successful implementation of the IMF-backed program and prudent monetary policy. The policy mix, while containing the short-term pain of utility price adjustments, is structurally beneficial. The tax reforms are designed to boost the supply side of the economy, while the stable Cedi and falling interest rates are stimulating demand and investment.
The following qualitative assessment summarizes the directional impact of the key policy components:
The analysis suggests that the combined effect of the policies will lead to a more stable and predictable economic environment in 2026, with lower inflation and interest rates paving the way for sustained GDP growth.
References
[1] EY Global. Ghana's finance minister presents 2025 budget statement and economic policy for FY2025 with tax implications. [https://www.ey.com/en_gl/technical/tax-alerts/ghanas-finance-minister-presents-2025-budget-statement-and-economic-policy-for-fy2025-with-tax-implications]
[2] The High Street Journal. Some OMCs Cut Fuel Prices as Cedi Strength and Global Oil Trends Ease Costs. [https://thehighstreetjournal.com/some-omcs-cut-fuel-prices-as-cedi-strength-and-global-oil-trends-ease-costs/]
[3] Fitch Ratings. Fitch Upgrades Ghana to 'B-'; Outlook Stable. [https://www.fitchratings.com/research/sovereigns/fitch-upgrades-ghana-to-b-outlook-stable-16-06-2025]
[4] Statista. Growth of the real gross domestic product (GDP) in Ghana from 1980 to 2030. [https://www.statista.com/statistics/447479/gross-domestic-product-gdp-growth-rate-in-ghana/?srsltid=AfmBOoqx92F9krzw4ejZSRJ95oBYHRv18u_Xw71orGcbV9_LJmBC6Zih]
[5] Trading Economics. Ghana Inflation Rate. [https://tradingeconomics.com/ghana/inflation-cpi]
[6] Reuters. Ghana central bank delivers third big rate cut as inflation tumbles. [https://www.reuters.com/world/africa/ghana-central-bank-delivers-third-big-rate-cut-inflation-tumbles-2025-11-26/]
[7] S&P Global. Research Update: Ghana Upgraded To 'B-/B' On Impr. [https://www.spglobal.com/ratings/en/regulatory/article/-/view/type/HTML/id/3475292]
[8] News Ghana. January Economic Reality Strips Ghana Households Of December Optimism. [https://www.newsghana.com.gh/january-economic-reality-strips-ghana-households-of-december-optimism/]
[9] MyJoyOnline. New Year begins with 15.92% water and 9.86% electricity tariff hikes. [https://www.myjoyonline.com/new-year-begins-with-15-92-water-and-9-86-electricity-tariff-hikes/]
[10] GBC Ghana Online. Fuel pump prices set for marginal decline as Cedi gains. [https://www.gbcghanaonline.com/news/business/fuel-pump-prices-set-for-marginal-decline-as-cedi-gains-crude-prices-fall-from-january-1-2026/2025/]
By : Emmanuel Danso-Boafo
The writer is a financial professional.
Latest Stories
-
Upper West Regional Minister denies diverting education infrastructure projects from Issa to Daffiama
16 minutes -
When success becomes a target: Ghana’s music industry habit of tearing down its own
20 minutes -
Savannah Region inaugurates 10-member health committee to reset sector
36 minutes -
Let’s demonstrate Mahama’s peace advocacy in his home region – Fulbe to chiefs and people
43 minutes -
Bright Ofori: Commending judicial reforms while advancing conversation on timely justice
57 minutes -
Newsfile to tackle security recruitment cuts, GH¢21bn audit exposé, Mahama jet controversy
1 hour -
Vice President receives UCC’s Distinguished Fellow Award, calls for education to deliver dev’t
2 hours -
Tension in DBI District as Issa chiefs demand reversal of relocated GES office
2 hours -
Women at the forefront: Celebrating Ghanaian women’s impact after 69 years of Independence
2 hours -
Gbeniyiri, Damongo violence: Security Councils condemn killings, vow to bring perpetrators to justice
2 hours -
KNUST declares five former students persona non grata, orders arrest on sight
3 hours -
Historic relief for Bono East as Holy Family Hospital receives first dialysis machines from GMTF
3 hours -
‘Pa-To-Pa’ promo is delivering on its promise – GCB Bank
3 hours -
Ghana Dance Industry Awards slated for April 18 at National Theatre
3 hours -
GCB Bank rewards 2nd and 3rd batch of winners in ‘Pa To Pa’ promo draw
3 hours

