Audio By Carbonatix
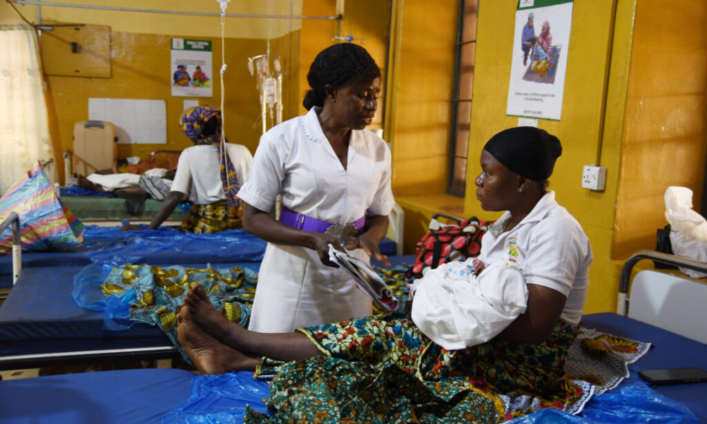
Health experts are raising alarm over the rapid rise of chronic diseases such as diabetes, stroke, and obesity across Africa, warning that without urgent investment in data systems and skills training, the continent risks falling further behind in disease prevention and treatment.
Speaking at the Data Science in Health (DS-I) meeting in Accra, researchers emphasized the need to tailor treatments to individual patient profiles and close skills gaps in order to strengthen disease prediction, prevention, and drug discovery.
“We have a diverse range of topics ranging from governance to drug discovery to nutrition to environmental health and climate change. The bottom line is that our findings are going to help drive innovations and unearth health discoveries on the continent,” he noted.
Professor Kofi Amegah, a Professor of Environmental and Nutritional Epidemiology at the University of Cape Coast, stressed that harnessing data could transform health delivery across the continent. He, however, cautioned that poor data quality, limited access, and funding constraints continue to impede progress.
“Data quality, access, and funding challenges have always been the big elephant in the room. These are the things that, if we want to leverage data science to improve health on the continent, governments will have to sit up, look at, and address,” he explained.
The DS-I discussions are part of a wider push to expand the role of artificial intelligence in healthcare, linking research institutions, universities, and health organizations in a collaborative effort to improve outcomes.
Professor Mayowa Owolabi, Director of the Center for Genomic and Precision Medicine at the University of Ibadan, urged African governments to embed data science into health policy, particularly to track and manage chronic diseases. He also described the withdrawal of USAID support as a significant setback for health initiatives on the continent.
“For the key non-communicable diseases like cardiovascular conditions, type 2 diabetes, and cancer, not much has been done. They’ve not been funded sufficiently to provide solutions that can reduce the burden. Right now, non-communicable diseases, particularly cardiovascular diseases, are the leading cause of death and disability on the African continent,” he warned.
As part of its roadmap, the Data Science in Health project aims to publish 18 manuscripts in leading journals and produce policy briefs for health ministries, the World Health Organization, and other key stakeholders.
Latest Stories
-
Rihanna’s Beverly Hills home hit by gunfire, police say
21 minutes -
Oil prices surge above $110 and shares slide over Iran war
31 minutes -
Surge in jet fuel prices could push up air fares, analysts warn
41 minutes -
Estupinan scores as ACR edge Inter in derby
4 hours -
Masked fan unplugs VAR monitor in German match
4 hours -
Teenage footballer dies during academy match in UK
4 hours -
Mahama heads to South Korea for high-level talks and business engagements
4 hours -
I will give marriage a second chance – Juliet Ibrahim
4 hours -
Alleged notorious land guard, accomplice arrested at Abokobi
4 hours -
Police arrest suspect at Aplaku over threat of death
5 hours -
Police arrest robbery suspect at Airport Residential Area
5 hours -
UK opens charter flights booking portal for Britons in Dubai
5 hours -
King Charles reflects on ‘pressures of conflict’ in Commonwealth message
5 hours -
Clubs complain to X about ‘sickening’ Grok posts
5 hours -
Rapper-politician Balendra Shah unseats Nepal’s ex-PM as he heads for victory
5 hours

