
Audio By Carbonatix
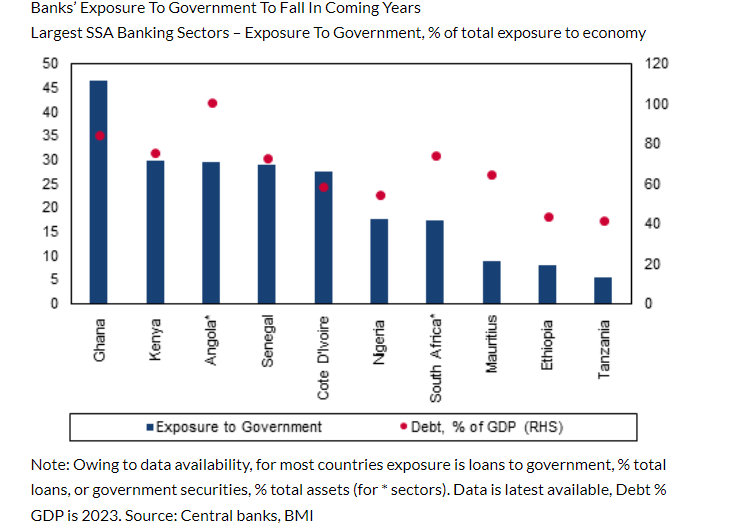
Ghana recorded the highest banks’ holdings of government debt in Sub Saharan Africa in 2023, Fitch Solutions has revealed.
In terms of government debt to Gross Domestic Product (GDP), the country came second behind Angola.
Kenya, South Africa and Senegal came 3rd, 4th and 5th respectively.
The report said banks in Sub-Saharan Africa including Ghana will continue to face risks associated with sovereign exposure throughout the forecast period. Nonetheless, these risks are expected to diminish over time.
During the Covid-19 pandemic, banks’ holdings of government debt and claims to the public sector surged as governments increased borrowing to fund additional expenditures.
With limited access to international markets owing to prohibitive costs, the report, said domestic banks became the main financiers. This dependence, it added, poses significant risks to banks, particularly when government finances are strained.
“This dependence poses significant risks to banks, particularly when government finances are strained. For instance, Ghana's default on its domestic and external debt in December 2022 led to considerable losses for banks participating in its domestic debt exchange programme”.
“As can be seen in the chart below, banking sectors in markets with elevated levels of government debt typically have the highest exposure to the government through loans or government securities holdings. We expect that the average debt-to-GDP ratio for the region will fall in the coming years, after peaking in 2023, boding well for our view that banks will reduce exposure to the sovereign”, it stressed.
Reopening of Africa’s Eurobond market in 2024 marks positive shift
The report continued that the reopening of Africa's Eurobond market in 2024, following a hiatus of more than a year, marks a positive shift, with successful, oversubscribed bond issuances from countries such as Côte d'Ivoire, Benin, and Kenya.
This resurgence, it said, provides government with a source of financing other than banks, offering banks the opportunity to lessen their exposure to sovereign debt, potentially liberating resources for increased lending to the private sector. However, this transition is expected to be gradual, as loan quality continues to be a concern and private sectors present higher risk profiles than sovereigns.
Latest Stories
-
Netherlands returns 3,500-year-old looted sculpture to Egypt
38 minutes -
‘Trump’s psyche’: The aide driving president’s most controversial policies
49 minutes -
Algeria begins to cancel air services agreement with UAE
1 hour -
Gunmen kill three people and abduct Catholic priest in northern Nigeria
1 hour -
‘I have not been the best dad lately – 2Face
4 hours -
Why top Nollywood stars were banned – Omotola Jalade Ekeinde
4 hours -
‘We don’t need to be best friends’ – Omotola speaks on alleged feud with Genevieve
5 hours -
MTN FA Cup: Defending champions Kotoko knocked out by Aduana
5 hours -
Why I no longer go clubbing – Davido
5 hours -
S Korean crypto firm accidentally pays out $40bn in bitcoin
5 hours -
Washington Post chief executive steps down after mass lay-offs
5 hours -
Iranian Nobel laureate handed further prison sentence, lawyer says
5 hours -
U20 WWCQ: South Africa come from behind to draw against Black Princesses in Accra
6 hours -
Why Prince William’s Saudi Arabia visit is a diplomatic maze
6 hours -
France murder trial complicated by twin brothers with same DNA
6 hours

