Audio By Carbonatix
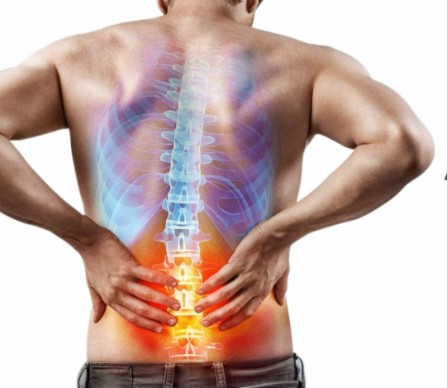
Low back pain (LBP) is a leading cause of disability worldwide, and health workers in Ghana are no exception.
A new study by researchers at the Kwame Nkrumah University of Science and Technology (KNUST) School of Public Health, conducted in the Greater Accra Region, has revealed that an alarming 81.6% of health workers suffer from LBP. Several job-related factors contribute to this high prevalence and are influencing many to consider leaving their jobs.
Published in the journal PLOS ONE, the study was conducted between January and May 2023 and involved 607 health workers from 10 public and private hospitals. It aimed to examine the prevalence, risk factors, and turnover intention associated with LBP among hospital staff.
The findings show that age, long working hours, overtime, and physical demands such as patient transfers are key contributors to the development of LBP. In addition, poor posture at work and perceptions of understaffing were also found to significantly increase the risk of injury.
Led by Dr. Philip Apraku Tawiah from the Department of Occupational and Environmental Health at the KNUST School of Public Health, the study revealed that advanced age, working more than five days a week, and frequently transferring patients significantly raised the likelihood of experiencing LBP.
Interestingly, health workers who reported sleeping more than eight hours a night or sitting intermittently during their shifts were less likely to suffer from LBP, suggesting that proper rest and ergonomic practices could help reduce the condition.
Beyond the physical toll, the study also identified a troubling link between LBP and turnover intention. Nearly a quarter of participants (24.9%) indicated that they occasionally considered leaving their jobs due to the pain they experienced.
“These highlights not only the physical burden but also the emotional and mental strain that LBP is placing on healthcare professionals in Ghana,” Dr. Tawiah said.
The researchers recommend “improving staffing levels, promoting ergonomic practices, and encouraging proper rest and posture to help reduce the incidence of LBP and support the overall well-being of health workers”.
Co-authors of this study are: Dr. Emmanuel Appiah-Brempong, Dr. Paul Okyere, Geoffrey Adu-Fosu and Dr. Mary Eyram Ashinyo.
Latest Stories
-
University of Ghana gears up for Telecel TurnUp on Val’s Day
3 minutes -
Violence against women is an economic catastrophe – President Mahama
8 minutes -
Contractor offers to repair damaged sections of Agona Nkwanta–Tarkwa Road Corridor at own cost
10 minutes -
Sinapi Aba Trust graduates 247 youth under its apprenticeship programme
11 minutes -
Concerned Farmers Association to announce position on new cocoa prices next week
16 minutes -
UNICEF encourages World Vision Ghana to remain a strong voice for children
20 minutes -
RTI Law: A triumph of legislative intent, tragedy of implementation
21 minutes -
Over 7,000 Muslims benefit from KSrelief food basket initiative in Ghana
28 minutes -
Sunda Group supports government’s free sanitary pad initiative with 10,000 packs
54 minutes -
“Everybody looks at me differently; some say I’m pretty” – Abigail Anderson opens up on living with vitiligo
1 hour -
President Trump’s moment of opportunity and the world at a crossroads
1 hour -
Ghana Cocoa board moves toward economic independence amid $2.5 billion debt crisis
1 hour -
AGA Obuasi Mine & partners inspire girls at Asare Bediako SHS to pursue careers in STEM
1 hour -
The 2026 WAFCON tournament will continue – CAF
2 hours -
Ministry of Youth Development urges responsible celebrations ahead of Valentine’s Day
2 hours