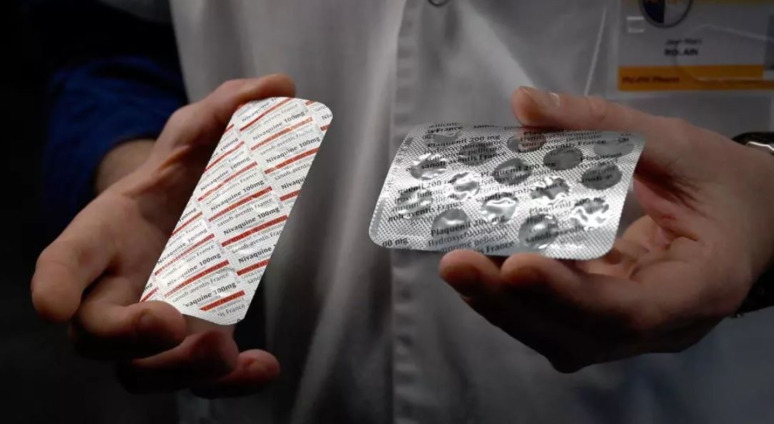
Long used as treatment for malaria and other ailments, chloroquine derivatives are being touted as a miracle cure in the fight against the worsening coronavirus pandemic. But the resulting surge in demand at French pharmacies has alarmed experts who warn against overhyping unproven medicines until large-scale clinical tests are carried out.
Chloroquine and its related compound, hydroxychloroquine, have been the focus of intense debate in France since a study conducted on a small number of COVID-19 patients in the southern city of Marseille yielded promising results.
On March 16, Professor Didier Raoult, the head of a university hospital institute in Marseille, announced his teams had treated 25 patients with hydroxychloroquine. After six days, he said, only one in four still had the virus in their body, whereas 90 percent of patients who had not taken the drug were still infected.
Raoult’s subsequent calls to expand the treatment, which garnered ample media attention, triggered a rush on French pharmacies – even as medical experts stressed the importance of first carrying out further trials on larger patient samples.
Philippe Besset, who heads the main representative body of French pharmacists, the FSPF, said pharmacies had witnessed a surge in demand for hydroxychloroquine, marketed by pharmaceutical giant Sanofi under the trade name Plaquénil.
“We’ve also witnessed a spike in the number of prescriptions for the drug,” he told FRANCE 24.
A similar increase in demand has been registered for the chloroquine-based drug Nivaquine, with the pharmaceutical wholesaler OPC reporting a 30-fold increase since the end of February, “when the first Covid-19 cases were reported in Europe and chloroquine-based clinical trials began attracting growing media coverage”.
Prescriptions without authorisation
Hydroxychloroquine is typically used to treat lupus, an auto-immune disease, and other chronic ailments such as rheumatoid arthritis.
“It’s a listed drug, meaning it can only be sold with a prescription,” said Carine Wolf-Thal, president of the French Chamber of Pharmacists, in an interview with FRANCE 24. “In theory, it can only be prescribed to treat illnesses that are listed by the regulatory body, such as lupus and polyarthritis.”
In practice, however, health professionals are allowed to issue prescriptions for other uses as well, so long as they are specified in the doctor’s notice, Wolf-Thal added.
“If the drug is prescribed in the context of the coronavirus pandemic, the prescription is issued under the doctor’s responsibility and must be labelled as such,” she explained. “It is this type of prescription that we have seen multiply in recent days.”
Depriving other patients of their only treatment
The rush for hydroxychloroquine has raised fear of a looming shortage of the drug, which could have catastrophic consequences for patients who relied on it long before it was associated with coronavirus treatment.
As Johanna Clouscard, who heads the patients’ association Lupus France, told France Info radio, “Plaquénil is the basic treatment against our disease.”
The two pills she takes every day help stave off skin rashes, joint pains and other inflammations associated with the auto-immune disease. Her association says there have been several reports of patients having trouble finding the drug.
While Besset of the FSPF confirmed that chloroquine stocks are running low in France's pharmacies, Wolf-Thal cautioned against talk of a shortage of the drug.
“Pharmacies are not allowed to stock-pile the drug,” she explained. “Their orders are limited by the wholesalers, precisely to avoid any shortage.”
>> Will an old malaria drug help fight the coronavirus?
The industry has also moved to allay patients’ concerns, with Sanofi announcing it has put in place a hotline for pharmacists to ensure the drug is made available to patients in urgent need.
“The procedure now requires greater transparency,” said Besset. “Pharmacies must contact the pharmaceutical labs directly and present a prescription, dated for January or February, that proves the patient has a chronic condition.”
On Monday, March 23, Health Minister Olivier Véran announced stricter guidelines to regulate sales of chloroquine and its related compounds. Under the new rules, the drugs “can only be used in test trials or in hospital care”, Wolf-Thal explained. “Their use will be limited to people who really need them and whose prescriptions comply with regulatory standards.”
The dangers of self-medication
On its website, the French Society of Pharmacology and Therapeutics notes that both chloroquine and hydroxychloroquine have a narrow margin of safety, meaning that effective doses and toxic doses are relatively close. That is why the experts contacted by FRANCE 24 warn against using them as self-medication to fight off COVID-19.
“Both the package leaflet for hydroxychloroquine and the guidelines issued by the [French] drugs watchdog detail the frequent side-effects associated with its use, such as deteriorating eyesight, nausea and digestive disorders,” said Besset. “More rarely – and far more dangerously – they can lead to heart failure.”
Aside from the drugs’ possible toxicity, experts warn that the excessive focus on chloroquine derivatives has overshadowed other treatments that may be more effective.
“It’s as if chloroquine had become the miracle cure that would save us all, when in fact there are other treatments too, particularly anti-viral and retro-viral ones,” said Wolf-Thal.
“For patients who suffer from mild forms of COVID-19, accounting for 85 percent of cases, paracetamol will suffice. There is no need to expose them to the risks and side-effects of chloroquine,” she added. “In more serious cases, it is up to health professionals to determine whether chloroquine is the appropriate treatment, based on the patients’ condition and general health. We must place our faith in hospital workers and medical research.”
This article was adapted from the original in French.
Latest Stories
-
Togbe Afede XIV calls for drastic restructuring of Bank of Ghana
43 mins -
Eric Johnson
52 mins -
Djokovic struck by water bottle at Italian Open
55 mins -
777 call in finance experts as Everton uncertainty grows
59 mins -
Casemiro left out of Brazil squad for Copa America
1 hour -
Chelsea sacking would not be a problem – Pochettino
1 hour -
Man Utd owners have ‘common sense’ – Ten Hag
1 hour -
Nduom hints at #BringBackGNBank nationwide campaign
5 hours -
GWCL staff locked up, assaulted for disconnecting defaulter
6 hours -
Akufo-Addo, Asantehene commission Prempeh I International Airport, Kumasi
6 hours -
We are confident about board meeting in June on Ghana’s second review – IMF
6 hours -
Eugene Osei Tutu: Who can lay claim to Kumasi International Airport- Mahama or Akufo-Addo?
6 hours -
Mbappe confirms he will leave Paris St-Germain
6 hours -
CAA Region II Athletics Championships will be properly organised – Dr Baah-Nuakoh
7 hours -
Over 185 state bungalows for public servants near completion in Ashanti Region
7 hours